# File Systems <!-- .element: class="r-fit-text" --> Week 9 --- ## Review  <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> -- ### How Does a Computer Store Information? <!-- .element: class="r-fit-text" --> It represents all data with **binary** numbers and organizes it into **files**. <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> -- ### Storage vs. Memory **Storage** is _persistent_, **memory** is _volatile_. <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> --- ## Bits and Bytes  <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> -- ### Bits A bit is a single binary digit: either 0 or 1. -- ### Bytes A byte is 8 bits. `00000000` is 0 in decimal <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> `11111111` is 255 in decimal <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> NOTES: why 8? because it's a power of 2 (2^3) -- ### Bigger Numbers - B = byte - KB = kilobyte (1000 B) - MB = megabyte (1000 MB) - GB = gigabyte (1000 MB) - TB = terabyte (1000 GB) NOTES: there are higher numbers like petabyte but they aren't as common -- ### Kilobits vs. Kilobytes 8 kilobits = 1 kilobyte 1Kb = 1/8 KB = 0.125 KB <!-- https://www.lifewire.com/what-is-a-megabit-2483412 --> -- ### Kibibytes vs. Kilobytes A “kibibyte” (KiB) is equal to 1024, or 2^10, bytes <!-- https://www.logicmonitor.com/blog/what-the-hell-is-a-kibibyte --> -- ### Review How many bits in a byte? _8_ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> How many bytes in a kilobyte? _1000_ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> Is Kb the same as KB? _No!_ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> Is KiB the same as KB? _No!_ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> --- ## Storing Primitives  <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> -- ### Booleans ```py True # 1 False # 0 ``` -- ### Integers ```py 1 # 00000001 100 # 01100100 255 # 11111111 ``` What about negative numbers? <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> -- ### Signed Integers ```py 1 # 00000001 100 # 01100100 -100 # 10011100 -127 # 10000001 127 # 01111111 ``` -- ### Floating Point Numbers _sign field_ | _exponent field_ | _significand field_ ```py 1 # 0 01111111 00000000000000000000000 100 # 0 10000101 10010000000000000000000 255 # 0 10000110 11111110000000000000000 ``` --- ## Storing Files  <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> -- ### Text Files (.txt)  -- ### Image Files (.png) <!--  -->  <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> -- ## Image Files 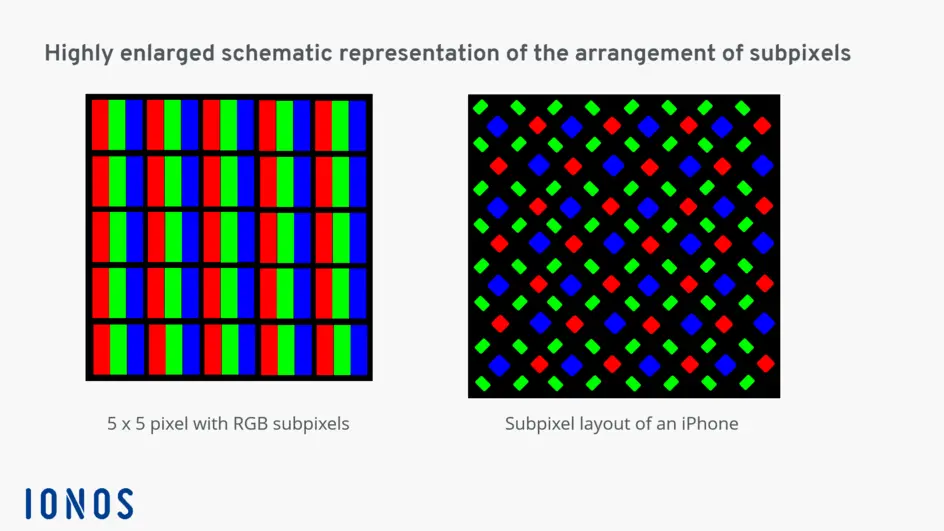 <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> NOTES: - If all three primary colors have the maximum value of 255, white appears - The values in between allow around 16.7 million shades of color (2563) to be displayed <!-- https://www.ionos.com/digitalguide/websites/web-design/what-is-a-pixel/ --> --- ## File Systems  <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> NOTES: in a previous quiz, you were asked how you would organize a library. This is the difficult question behind file systems. -- ### Considerations - Performance - Integrity - Scalability - Compatibility - Security NOTES: - Faster w/large files or many small files? - Checksums or redundancy? - What happens when you add more storage? - Not all computers use the same - Encryption, permissions, etc. <!-- https://hivo.co/blog/a-tour-of-file-system-types-choosing-the-right-fit-for-your-needs --> -- ### Common Types - FAT (File Allocation Table) - NTFS (New Technology File System) - ext4 (Fourth Extended File System) - APFS (Apple File System) NOTES: - NTFS most common for Windows - APFS most common for macOS - ext4 most common for Linux -- ### Types of Files - File (data) - Directory (folder) -- ### Paths Windows: `C:\Users\Rylan` Unix: `/Users/Rylan` -- ### Fragmentation  <!-- .element: style="height:400px" --> NOTES: - _Spatial_ (reference) locality is how close files are - Takes longer to get to your aunt's house than your friend's - Keep it closer to keep it fast - Defragmentation re-organizes to keep common stuff close - Other options include _temperal_ locality -- ### Review Are all file systems the same? _No!_ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> What are some considerations when picking a file system? _Performance, integrity, scalability, compatibility, security._ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> What is a file path? _All folders plus the file name._ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> What is fragmentation and why is it bad? _Separation of files, slows down R/W operations._ <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> --- ## Now for Some Coding... <!-- .element: class="r-fit-text" --> [Python: Reading/Writing Files](/2024/fall/computer-science/slides/python-files)